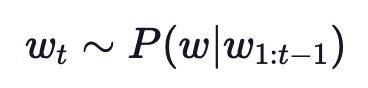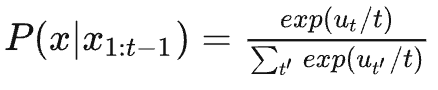👉导读
👉目录
01
02
2.1 原理介绍
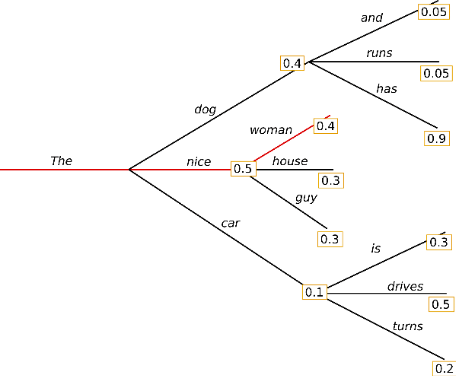
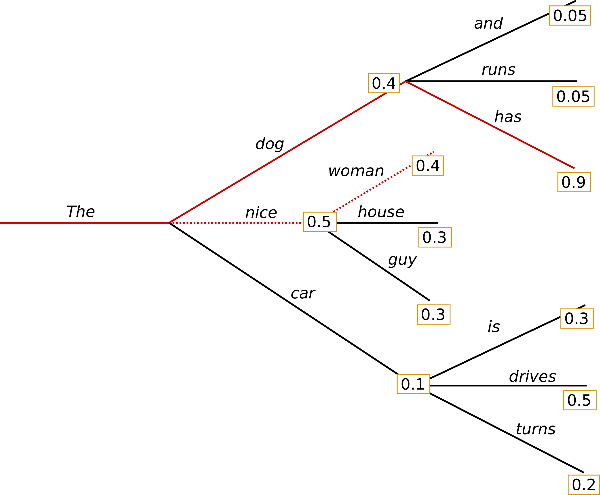
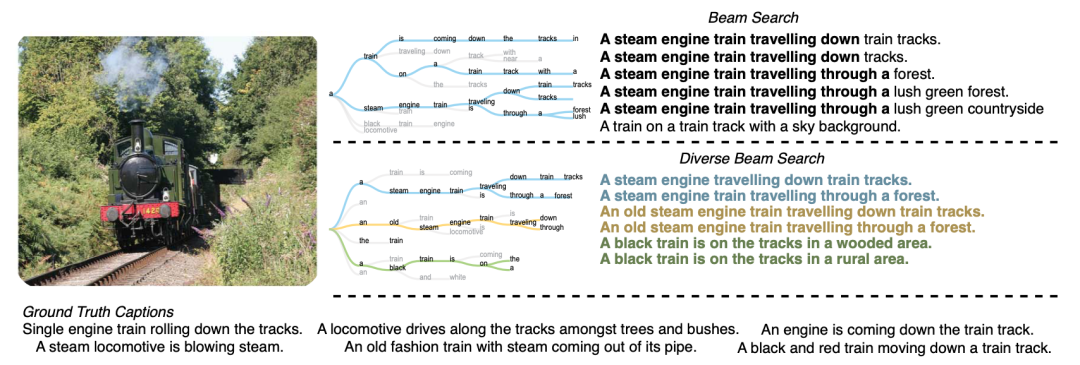
最简单的策略就是 greedy decoding,即每步选择概率最大的 token: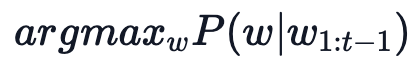 。如上图所示,从单词 The 开始,该策略每步都会选择下一步概率最大的词,最后会得到输出序列 The nice woman,总概率是 0.5 * 0.4 = 0.2。greedy decoding 速度最快,也有如下几个缺点:
。如上图所示,从单词 The 开始,该策略每步都会选择下一步概率最大的词,最后会得到输出序列 The nice woman,总概率是 0.5 * 0.4 = 0.2。greedy decoding 速度最快,也有如下几个缺点:
|
一、 它可能会错过全局概率最大的序列。比如上图中,The dog has 的总概率更大,是0.4 * 0.9 = 0.36。 二、 由于缺少随机性,模型在输出一个重复的 token 之后,有较大可能陷入重复输出序列的循环。 三、 greedy 解码方式非常接近模型训练时候的 objective,因此容易复述训练数据,缺少了创造性。 |
2.2 快速上手
# 环境:python3.9、torch1.13.1、transformers4.26.1from transformers import (AutoTokenizer,AutoModelForCausalLM,LogitsProcessorList,MinLengthLogitsProcessor,RepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor,StoppingCriteriaList,MaxLengthCriteria,)tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2")# set pad_token_id to eos_token_id because GPT2 does not have a PAD tokenmodel.generation_config.pad_token_id = model.generation_config.eos_token_idinput_prompt = "It might be possible to"input_ids = tokenizer(input_prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids# instantiate logits processorslogits_processor = LogitsProcessorList([MinLengthLogitsProcessor(10, eos_token_id=model.generation_config.eos_token_id),RepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor(1.2),])stopping_criteria = StoppingCriteriaList([MaxLengthCriteria(max_length=20)])outputs = model.greedy_search(input_ids, logits_processor=logits_processor, stopping_criteria=stopping_criteria)result = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)print(result)-------------------------------------------------output-------------------------------------------------['It might be possible to get a better understanding of the nature of this phenomenon, but it is not']
快速上手的代码参考:Generation,更详细的参数介绍也可从中获取。
链接:https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/text_generation
2.3 代码解读
主要针对快速上手的第30-32行代码调用的 greedy_search 方法进行解读。
代码地址:
2.3.1 基本设置,对后续需要使用的变量进行初始化
logits_processor = logits_processor if logits_processor is not None else LogitsProcessorList()stopping_criteria = stopping_criteria if stopping_criteria is not None else StoppingCriteriaList()if max_length is not None:warnings.warn("`max_length` is deprecated in this function, use"" `stopping_criteria=StoppingCriteriaList([MaxLengthCriteria(max_length=max_length)])` instead.",UserWarning,)stopping_criteria = validate_stopping_criteria(stopping_criteria, max_length)pad_token_id = pad_token_id if pad_token_id is not None else self.generation_config.pad_token_ideos_token_id = eos_token_id if eos_token_id is not None else self.generation_config.eos_token_idif isinstance(eos_token_id, int):eos_token_id = [eos_token_id]output_scores = output_scores if output_scores is not None else self.generation_config.output_scoresoutput_attentions = (output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.generation_config.output_attentions)output_hidden_states = (output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.generation_config.output_hidden_states)return_dict_in_generate = (return_dict_in_generateif return_dict_in_generate is not Noneelse self.generation_config.return_dict_in_generate)# init attention / hidden states / scores tuplesscores = () if (return_dict_in_generate and output_scores) else Nonedecoder_attentions = () if (return_dict_in_generate and output_attentions) else Nonecross_attentions = () if (return_dict_in_generate and output_attentions) else Nonedecoder_hidden_states = () if (return_dict_in_generate and output_hidden_states) else None# if model is an encoder-decoder, retrieve encoder attention weights and hidden statesif return_dict_in_generate and self.config.is_encoder_decoder:encoder_attentions = model_kwargs["encoder_outputs"].get("attentions") if output_attentions else Noneencoder_hidden_states = (model_kwargs["encoder_outputs"].get("hidden_states") if output_hidden_states else None)
|
|
2.3.2 从 bos_token 开始解码
# keep track of which sequences are already finishedunfinished_sequences = input_ids.new(input_ids.shape[0]).fill_(1)this_peer_finished = False # used by synced_gpus onlywhile True:if synced_gpus:# Under synced_gpus the `forward` call must continue until all gpus complete their sequence.# The following logic allows an early break if all peers finished generating their sequencethis_peer_finished_flag = torch.tensor(0.0 if this_peer_finished else 1.0).to(input_ids.device)# send 0.0 if we finished, 1.0 otherwisedist.all_reduce(this_peer_finished_flag, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)# did all peers finish? the reduced sum will be 0.0 thenif this_peer_finished_flag.item() == 0.0:break# prepare model inputsmodel_inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids, **model_kwargs)# forward pass to get next tokenoutputs = self(**model_inputs,return_dict=True,output_attentions=output_attentions,output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,)if synced_gpus and this_peer_finished:continue # don't waste resources running the code we don't neednext_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :]# pre-process distributionnext_tokens_scores = logits_processor(input_ids, next_token_logits)# Store scores, attentions and hidden_states when requiredif return_dict_in_generate:if output_scores:scores += (next_tokens_scores,)if output_attentions:decoder_attentions += ((outputs.decoder_attentions,) if self.config.is_encoder_decoder else (outputs.attentions,))if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:cross_attentions += (outputs.cross_attentions,)if output_hidden_states:decoder_hidden_states += ((outputs.decoder_hidden_states,)if self.config.is_encoder_decoderelse (outputs.hidden_states,))# argmaxnext_tokens = torch.argmax(next_tokens_scores, dim=-1)# finished sentences should have their next token be a padding tokenif eos_token_id is not None:if pad_token_id is None:raise ValueError("If `eos_token_id` is defined, make sure that `pad_token_id` is defined.")next_tokens = next_tokens * unfinished_sequences + pad_token_id * (1 - unfinished_sequences)# update generated ids, model inputs, and length for next stepinput_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens[:, None]], dim=-1)model_kwargs = self._update_model_kwargs_for_generation(outputs, model_kwargs, is_encoder_decoder=self.config.is_encoder_decoder)# if eos_token was found in one sentence, set sentence to finishedif eos_token_id is not None:unfinished_sequences = unfinished_sequences.mul((sum(next_tokens != i for i in eos_token_id)).long())# stop when each sentence is finished, or if we exceed the maximum lengthif unfinished_sequences.max() == 0 or stopping_criteria(input_ids, scores):if not synced_gpus:breakelse:this_peer_finished = True
|
30-33行:获取 next_token_logits,维度为[batch_size, vocab_size],即预测的下一个 token 的 logits。之后调用1.中初始化的 logits_processor 对 next_token_logits 进行预处理,logits_processor 为 LogitsProcessorList 的实例。 |
class LogitsProcessorList(list):"""This class can be used to create a list of [`LogitsProcessor`] or [`LogitsWarper`] to subsequently process a`scores` input tensor. This class inherits from list and adds a specific *__call__* method to apply each[`LogitsProcessor`] or [`LogitsWarper`] to the inputs."""@add_start_docstrings(LOGITS_PROCESSOR_INPUTS_DOCSTRING)def __call__(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor, scores: torch.FloatTensor, **kwargs) -> torch.FloatTensor:for processor in self:function_args = inspect.signature(processor.__call__).parametersif len(function_args) > 2:if not all(arg in kwargs for arg in list(function_args.keys())[2:]):raise ValueError(f"Make sure that all the required parameters: {list(function_args.keys())} for "f"{processor.__class__} are passed to the logits processor.")scores = processor(input_ids, scores, **kwargs)else:scores = processor(input_ids, scores)return scores
|
10-21行:循环调用 LogitsProcessor 中的 processor。对于每一次循环,首先获取 processor __call__方法的参数,若参数个数大于2,对参数进行检查,确保所有参数都正确传入了,之后再进行调用。若参数个数小于等于2,则直接调用。最后返回处理后的得分。 |
这里介绍快速上手中使用的两种预处理方法最小长度和重复词惩罚对应的 processor。
· 最小长度
代码:transformers/logits_process.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
class MinLengthLogitsProcessor(LogitsProcessor):r"""[`LogitsProcessor`] enforcing a min-length by setting EOS probability to 0.Args:min_length (`int`):The minimum length below which the score of `eos_token_id` is set to `-float("Inf")`.eos_token_id (`Union[int, List[int]]`):The id of the *end-of-sequence* token. Optionally, use a list to set multiple *end-of-sequence* tokens."""def __init__(self, min_length: int, eos_token_id: Union[int, List[int]]):if not isinstance(min_length, int) or min_length < 0:raise ValueError(f"`min_length` has to be a positive integer, but is {min_length}")if isinstance(eos_token_id, int):eos_token_id = [eos_token_id]if not all([isinstance(i, int) for i in eos_token_id]) or any([i < 0 for i in eos_token_id]):raise ValueError(f"`eos_token_id` has to be a list of positive integers, but is {eos_token_id}")self.min_length = min_lengthself.eos_token_id = eos_token_iddef __call__(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor, scores: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:cur_len = input_ids.shape[-1]if cur_len < self.min_length:for i in self.eos_token_id:scores[:, i] = -float("inf")return scores
|
|
· 重复词惩罚
代码:transformers/logits_process.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
class RepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor(LogitsProcessor):r"""[`LogitsProcessor`] enforcing an exponential penalty on repeated sequences.Args:repetition_penalty (`float`):The parameter for repetition penalty. 1.0 means no penalty. See [thispaper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.05858.pdf) for more details."""def __init__(self, penalty: float):if not isinstance(penalty, float) or not (penalty > 0):raise ValueError(f"`penalty` has to be a strictly positive float, but is {penalty}")self.penalty = penaltydef __call__(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor, scores: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:score = torch.gather(scores, 1, input_ids)# if score < 0 then repetition penalty has to be multiplied to reduce the previous token probabilityscore = torch.where(score < 0, score * self.penalty, score / self.penalty)scores.scatter_(1, input_ids, score)return scores
|
|
2.3.3 解码结束,返回结果
if return_dict_in_generate:if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:return GreedySearchEncoderDecoderOutput(sequences=input_ids,scores=scores,encoder_attentions=encoder_attentions,encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,decoder_attentions=decoder_attentions,cross_attentions=cross_attentions,decoder_hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return GreedySearchDecoderOnlyOutput(sequences=input_ids,scores=scores,attentions=decoder_attentions,hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return input_ids
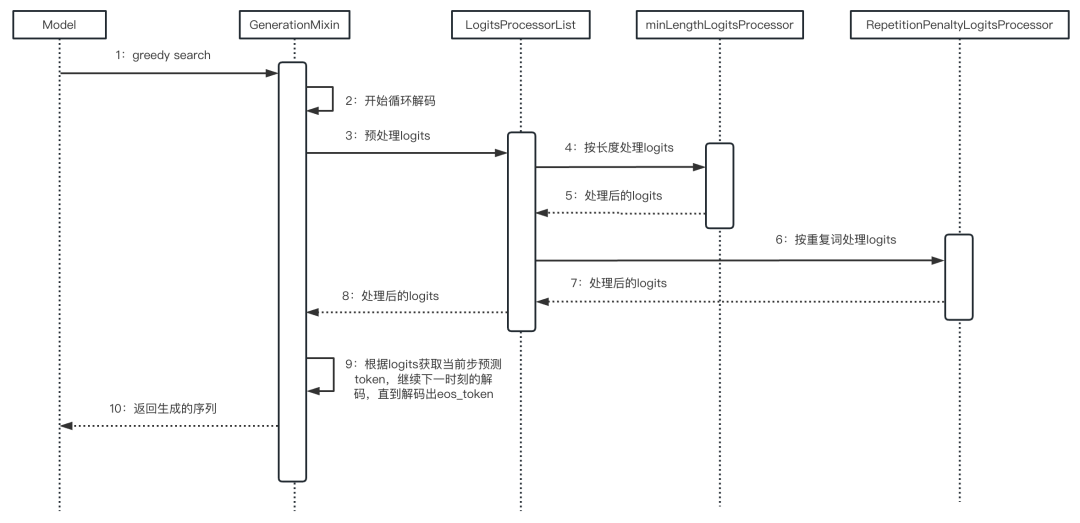
2.4 整体流程
整体流程如下面的时序图所示
03
3.1 原理介绍
为了解决 greedy decoding 可能错过全局最大概率序列的问题,beam search 策略经常会被采用,即维护 beam=n,保留当前最佳的n个序列,并且对于每个序列,都在计算最好的 n 个 next token,然后再从 n*n 个结果中,保留 n 个概率乘积最大的序列。比如上图中,假设 beam=2,从 The 开始,会保留[The dog, The nice]两个序列,接着每个序列选取2个最佳的next token,得到4个序列,再从中选择2个最佳序列[The dog has, The nice woman]。然而,beam Search 有以下缺点:
|
一、 在 text generation 中,一般将[EOS] token 视为文本的结尾,也就是 absorbing state。如果某个候选序列达到这个 absorbing state,就不再扩展它。这就会造成 Beam Search 通常会倾向于更短的序列,因为长序列算概率乘积后,数值会相对短序列更小。因此,一般会在得分函数中引入 length normalization 对长度进行归一化。 常见方法是引入𝛼∈[0,1],𝛼=0不归一化。𝛼=1,标准的长度归一化。
二、 由于缺少随机性,beam search 仍然很可能掉入重复序列的循环。因而一些工作引入了 n-grams penalty 来缓解。最常见的方法是通过将已经看到的 n-gram 的下一个单词的概率设置为0,来确保没有 n-gram 出现两次。n 是一个超参数,如果 n 设为2,则 2-gram 序列,比如 New York 不会在解码中出现两次。 三、 最后,相比于人类语句一般不太可预测,beam search 生成的序列缺少惊喜,因此在需要创造性的生成场景中不是非常合适。
|
3.2 快速上手
from transformers import (AutoTokenizer,AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,LogitsProcessorList,NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor,BeamSearchScorer,)import torchtokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-base")model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-base")encoder_input_str = "translate English to Chinese: How old are you?"encoder_input_ids = tokenizer(encoder_input_str, return_tensors="pt").input_ids# lets run beam search using 3 beamsnum_beams = 3# define decoder start token idsinput_ids = torch.ones((num_beams, 1), device=model.device, dtype=torch.long)input_ids = input_ids * model.config.decoder_start_token_id# add encoder_outputs to model keyword argumentsmodel_kwargs = {"encoder_outputs": model.get_encoder()(encoder_input_ids.repeat_interleave(num_beams, dim=0), return_dict=True)}# instantiate beam scorerbeam_scorer = BeamSearchScorer(batch_size=1,num_beams=num_beams,num_beam_hyps_to_keep=2,device=model.device,)# instantiate logits processorslogits_processor = LogitsProcessorList([NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor(2),])outputs = model.beam_search(input_ids, beam_scorer, logits_processor=logits_processor, **model_kwargs)result = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))print(result)-------------------------------------------------output-------------------------------------------------['Wie alt bist du?']
3.3 代码解读
3.3.1 基本设置,对后续需要使用的变量进行初始化
batch_size = len(beam_scorer._beam_hyps)num_beams = beam_scorer.num_beamsbatch_beam_size, cur_len = input_ids.shapeif num_beams * batch_size != batch_beam_size:raise ValueError(f"Batch dimension of `input_ids` should be {num_beams * batch_size}, but is {batch_beam_size}.")beam_indices = (tuple(() for _ in range(batch_beam_size)) if (return_dict_in_generate and output_scores) else None)
这一步与 greedy search 基本一致,区别在于需要额外初始化一些用于 beam search 的变量。
|
|
3.3.2 从 bos_token 开始解码
# initialise score of first beam with 0 and the rest with -1e9. This makes sure that only tokens# of the first beam are considered to avoid sampling the exact same tokens across all beams.beam_scores = torch.zeros((batch_size, num_beams), dtype=torch.float, device=input_ids.device)beam_scores[:, 1:] = -1e9beam_scores = beam_scores.view((batch_size * num_beams,))this_peer_finished = False # used by synced_gpus onlywhile True:if synced_gpus:# Under synced_gpus the `forward` call must continue until all gpus complete their sequence.# The following logic allows an early break if all peers finished generating their sequencethis_peer_finished_flag = torch.tensor(0.0 if this_peer_finished else 1.0).to(input_ids.device)# send 0.0 if we finished, 1.0 otherwisedist.all_reduce(this_peer_finished_flag, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)# did all peers finish? the reduced sum will be 0.0 thenif this_peer_finished_flag.item() == 0.0:breakmodel_inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids, **model_kwargs)outputs = self(**model_inputs,return_dict=True,output_attentions=output_attentions,output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,)if synced_gpus and this_peer_finished:cur_len = cur_len + 1continue # don't waste resources running the code we don't neednext_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :]# hack: adjust tokens for Marian. For Marian we have to make sure that the `pad_token_id`# cannot be generated both before and after the `nn.functional.log_softmax` operation.next_token_logits = self.adjust_logits_during_generation(next_token_logits, cur_len=cur_len)next_token_scores = nn.functional.log_softmax(next_token_logits, dim=-1) # (batch_size * num_beams, vocab_size)next_token_scores_processed = logits_processor(input_ids, next_token_scores)next_token_scores = next_token_scores_processed + beam_scores[:, None].expand_as(next_token_scores)# Store scores, attentions and hidden_states when requiredif return_dict_in_generate:if output_scores:scores += (next_token_scores_processed,)if output_attentions:decoder_attentions += ((outputs.decoder_attentions,) if self.config.is_encoder_decoder else (outputs.attentions,))if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:cross_attentions += (outputs.cross_attentions,)if output_hidden_states:decoder_hidden_states += ((outputs.decoder_hidden_states,)if self.config.is_encoder_decoderelse (outputs.hidden_states,))# reshape for beam searchvocab_size = next_token_scores.shape[-1]next_token_scores = next_token_scores.view(batch_size, num_beams * vocab_size)# Sample 2 next tokens for each beam (so we have some spare tokens and match output of beam search)next_token_scores, next_tokens = torch.topk(next_token_scores, 2 * num_beams, dim=1, largest=True, sorted=True)next_indices = torch_int_div(next_tokens, vocab_size)next_tokens = next_tokens % vocab_size# statelessbeam_outputs = beam_scorer.process(input_ids,next_token_scores,next_tokens,next_indices,pad_token_id=pad_token_id,eos_token_id=eos_token_id,beam_indices=beam_indices,)beam_scores = beam_outputs["next_beam_scores"]beam_next_tokens = beam_outputs["next_beam_tokens"]beam_idx = beam_outputs["next_beam_indices"]input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids[beam_idx, :], beam_next_tokens.unsqueeze(-1)], dim=-1)model_kwargs = self._update_model_kwargs_for_generation(outputs, model_kwargs, is_encoder_decoder=self.config.is_encoder_decoder)if model_kwargs["past_key_values"] is not None:model_kwargs["past_key_values"] = self._reorder_cache(model_kwargs["past_key_values"], beam_idx)if return_dict_in_generate and output_scores:beam_indices = tuple((beam_indices[beam_idx[i]] + (beam_idx[i],) for i in range(len(beam_indices))))# increase cur_lencur_len = cur_len + 1if beam_scorer.is_done or stopping_criteria(input_ids, scores):if not synced_gpus:breakelse:this_peer_finished = Truesequence_outputs = beam_scorer.finalize(input_ids,beam_scores,next_tokens,next_indices,pad_token_id=pad_token_id,eos_token_id=eos_token_id,max_length=stopping_criteria.max_length,beam_indices=beam_indices,)
|
1-5行:初始化 beam_scores,维度为[batch_size, num_beams],首先赋值为0,之后将除第一条候选路径之外的路径分数均赋值为-1e9,在7)中将会介绍这么做的原因,最后将维度变换为[batch_size * num_beams],方便后续的矩阵运算; 7-32行:与 greedy search 基本一致; 33-35行:针对 Marian 模型进行特殊处理,该模型不允许在进行 log_softmax 之前和之后生成 pad token; 36-41行:使用 log_softmax 对 next_token_logits 计算概率值。之后对 next_token_scores 进行预处理。最后将预处理后的当前预测 token 的得分与之前预测序列的得分相加,作为该候选路径的当前得分。这里对快速上手中用到的 n-gram 惩罚预处理进行介绍。 |
代码:
transformers/logits_process.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
class NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor(LogitsProcessor):r"""[`LogitsProcessor`] that enforces no repetition of n-grams. See[Fairseq](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/blob/a07cb6f40480928c9e0548b737aadd36ee66ac76/fairseq/sequence_generator.py#L345).Args:ngram_size (`int`):All ngrams of size `ngram_size` can only occur once."""def __init__(self, ngram_size: int):if not isinstance(ngram_size, int) or ngram_size <= 0:raise ValueError(f"`ngram_size` has to be a strictly positive integer, but is {ngram_size}")self.ngram_size = ngram_sizedef __call__(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor, scores: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:num_batch_hypotheses = scores.shape[0]cur_len = input_ids.shape[-1]banned_batch_tokens = _calc_banned_ngram_tokens(self.ngram_size, input_ids, num_batch_hypotheses, cur_len)for i, banned_tokens in enumerate(banned_batch_tokens):scores[i, banned_tokens] = -float("inf")return scores
|
|
def _calc_banned_ngram_tokens(ngram_size: int, prev_input_ids: torch.Tensor, num_hypos: int, cur_len: int) -> List[Iterable[int]]:"""Copied from fairseq for no_repeat_ngram in beam_search"""if cur_len + 1 < ngram_size:# return no banned tokens if we haven't generated no_repeat_ngram_size tokens yetreturn [[] for _ in range(num_hypos)]generated_ngrams = _get_ngrams(ngram_size, prev_input_ids, num_hypos)banned_tokens = [_get_generated_ngrams(generated_ngrams[hypo_idx], prev_input_ids[hypo_idx], ngram_size, cur_len)for hypo_idx in range(num_hypos)]return banned_tokens
|
|
def _get_ngrams(ngram_size: int, prev_input_ids: torch.Tensor, num_hypos: int):generated_ngrams = [{} for _ in range(num_hypos)]for idx in range(num_hypos):gen_tokens = prev_input_ids[idx].tolist()generated_ngram = generated_ngrams[idx]for ngram in zip(*[gen_tokens[i:] for i in range(ngram_size)]):prev_ngram_tuple = tuple(ngram[:-1])generated_ngram[prev_ngram_tuple] = generated_ngram.get(prev_ngram_tuple, []) + [ngram[-1]]return generated_ngrams
|
2-2行:为每个样本初始化一个 dict,用来保存已经生成的 ngram; |
>>> gen_tokens = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]>>> for i in range(2):... print(gen_tokens[i:])...[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10][2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]>>> for ngram in zip(*[gen_tokens[i:] for i in range(2)]):... print(ngram)...(1, 2)(2, 3)(3, 4)(4, 5)(5, 6)(6, 7)(7, 8)(8, 9)(9, 10)
|
|
def _get_generated_ngrams(banned_ngrams, prev_input_ids, ngram_size, cur_len):# Before decoding the next token, prevent decoding of ngrams that have already appearedstart_idx = cur_len + 1 - ngram_sizengram_idx = tuple(prev_input_ids[start_idx:cur_len].tolist())return banned_ngrams.get(ngram_idx, [])
|
2-5行:start_idx 为已生成序列中最后一个 ngram 的起始位置,cur_len 为已生成序列中最后一个 ngram 除最后一个 token 外的结束位置,因此 prev_input_ids[start_idx: curlen] 即为最后一个 ngram 的前缀,用该前缀去 banned_grams 查找,若存在则获得当前步需要禁止生成的 token,否则为空。最后返回结果; |
代码:
transformers/beam_search.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
def process(self,input_ids: torch.LongTensor,next_scores: torch.FloatTensor,next_tokens: torch.LongTensor,next_indices: torch.LongTensor,pad_token_id: Optional[int] = None,eos_token_id: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,beam_indices: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor]:cur_len = input_ids.shape[-1]batch_size = len(self._beam_hyps)if not (batch_size == (input_ids.shape[0] // self.group_size)):if self.num_beam_groups > 1:raise ValueError(f"A group beam size of {input_ids.shape[0]} is used as the input, but a group beam "f"size of {self.group_size} is expected by the beam scorer.")else:raise ValueError(f"A beam size of {input_ids.shape[0]} is used as the input, but a beam size of "f"{self.group_size} is expected by the beam scorer.")device = input_ids.devicenext_beam_scores = torch.zeros((batch_size, self.group_size), dtype=next_scores.dtype, device=device)next_beam_tokens = torch.zeros((batch_size, self.group_size), dtype=next_tokens.dtype, device=device)next_beam_indices = torch.zeros((batch_size, self.group_size), dtype=next_indices.dtype, device=device)if isinstance(eos_token_id, int):eos_token_id = [eos_token_id]for batch_idx, beam_hyp in enumerate(self._beam_hyps):if self._done[batch_idx]:if self.num_beams < len(beam_hyp):raise ValueError(f"Batch can only be done if at least {self.num_beams} beams have been generated")if eos_token_id is None or pad_token_id is None:raise ValueError("Generated beams >= num_beams -> eos_token_id and pad_token have to be defined")# pad the batchnext_beam_scores[batch_idx, :] = 0next_beam_tokens[batch_idx, :] = pad_token_idnext_beam_indices[batch_idx, :] = 0continue# next tokens for this sentencebeam_idx = 0for beam_token_rank, (next_token, next_score, next_index) in enumerate(zip(next_tokens[batch_idx], next_scores[batch_idx], next_indices[batch_idx])):batch_beam_idx = batch_idx * self.group_size + next_index# add to generated hypotheses if end of sentenceif (eos_token_id is not None) and (next_token.item() in eos_token_id):# if beam_token does not belong to top num_beams tokens, it should not be addedis_beam_token_worse_than_top_num_beams = beam_token_rank >= self.group_sizeif is_beam_token_worse_than_top_num_beams:continueif beam_indices is not None:beam_index = beam_indices[batch_beam_idx]beam_index = beam_index + (batch_beam_idx,)else:beam_index = Nonebeam_hyp.add(input_ids[batch_beam_idx].clone(),next_score.item(),beam_indices=beam_index,)else:# add next predicted token since it is not eos_tokennext_beam_scores[batch_idx, beam_idx] = next_scorenext_beam_tokens[batch_idx, beam_idx] = next_tokennext_beam_indices[batch_idx, beam_idx] = batch_beam_idxbeam_idx += 1# once the beam for next step is full, don't add more tokens to it.if beam_idx == self.group_size:breakif beam_idx < self.group_size:raise ValueError(f"At most {self.group_size} tokens in {next_tokens[batch_idx]} can be equal to `eos_token_id:"f" {eos_token_id}`. Make sure {next_tokens[batch_idx]} are corrected.")# Check if we are done so that we can save a pad step if all(done)self._done[batch_idx] = self._done[batch_idx] or beam_hyp.is_done(next_scores[batch_idx].max().item(), cur_len)return UserDict({"next_beam_scores": next_beam_scores.view(-1),"next_beam_tokens": next_beam_tokens.view(-1),"next_beam_indices": next_beam_indices.view(-1),})
|
11-23行:参数检查,要求 batch_size 必须等于 input_ids.shape[0] * self.group_size,self._beam_hyps 保存 batch 内每条样本所有候选路径的解码结果,长度为 batch_size * num_beams,self.group_size 在此处等于 num_beams,后续遇到时用 num_beams 来代替,在另一种解码策略 group beam search 中会再进行详细介绍; 25-28行:next_beam_tokens 为当前步预测的 token,next_beam_scores 为预测 token 对应的路径的得分,next_beam_indices 为预测 token 所在路径的下标,维度均为 [batch_size, 2 * num_beams]; 30-31行:与 greedy search 相同; 33-33行:遍历 batch 内每个样本已生成的句子; 34-43行:若当前样本已解码完成,首先进行参数检查,已生成的句子个数不能小于 num_beams,eos_token_id 和 pad_token_id 不能同时为 None。因为已解码完成,所以将当前步预测 token 设为 pad token,对应的路径的得分和所在路径的下标设为0,这里可以设为0的原因是解码完成后,路径得分已存在 self._beam_hyps 中; 45-49行:遍历当前样本在当前步预测的2 * num_beams个token,以及其路径的得分和所在路径的下标; 50-50行:batch_beam_idx 为预测 token 在 batch 中的下标; 51-67行:若当前步预测的 token 在 eos_token 中,说明已解码完成,需要将其加入当前样本的生成结果中。首先,若 beam_token_rank 大于等于 num_beams,由于 score 是经过 log_softmax 运算得到的,是一个负数,因此后续不会再有路径的得分会大于当前步的前 num_beams 个路径的得分了,因此不需要再将该结果加入生成结果之中了。之后,beam_indices 为每个样本最后一个预测的 token 所在路径的每一步路径下标,是一个大小为 batch_size* num_beams 的元组,其中每个元素也是一个元组,若其不为空,则将当前步预测的 token 所在的路径加入对应的元组中; 63-67行:beam_hyp 用来存储当前样本的所有生成结果,若执行到该处,则将当前生成的结果加入该样本的 beam_hyp中。 |
def add(self, hyp: torch.LongTensor, sum_logprobs: float, beam_indices: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None):"""Add a new hypothesis to the list."""score = sum_logprobs / (hyp.shape[-1] ** self.length_penalty)if len(self) < self.num_beams or score > self.worst_score:self.beams.append((score, hyp, beam_indices))if len(self) > self.num_beams:sorted_next_scores = sorted([(s, idx) for idx, (s, _, _) in enumerate(self.beams)])del self.beams[sorted_next_scores[0][1]]self.worst_score = sorted_next_scores[1][0]else:self.worst_score = min(score, self.worst_score)
|
5-5行:计算 score,将所有生成的 token 的 logsoftmax 的值相加,再除以(长度 ** self.length_penalty),这个 score 也作为这条路径的最终得分,这里除以(长度 ** self.length_penalty)主要是为了增加或减少长度更长的序列的得分,当 self.length_penalty > 0 的时候,这一步的计算就会增加长度更长的序列的得分,self.length_penalty < 0 的时候反之;可以通过几个例子来看: |
eg1:假设self.length_penalty = 0序列1:今天天气很好(长度6,sum_logprobs=-0.6)那么score1 = -0.6 / 6 ** 0 = -0.6 / 1 = -0.6序列2:今天天气真的真的很好(长度10,sum_logprobs=-0.8)那么score2 = -0.8 / 10 ** 0 = -0.8 / 1 = -0.8此时score1 > score2,最终会选择长度更短的序列1eg2:假设self.length_penalty = 1序列1:今天天气很好(长度6,sum_logprobs=-0.6)那么score1 = -0.6 / 6 ** 1 = -0.6 / 6 = -0.1序列2:今天天气真的真的很好(长度10,sum_logprobs=-0.8)那么score2 = -0.8 / 10 ** 1 = -0.8 / 10 = -0.08此时score2 > score1,最终会选择长度更长的序列2eg3:假设self.length_penalty = 2候选1:今天天气很好(长度6,sum_logprobs=-0.6)那么score1 = -0.6 / 6 ** 2 = -0.6 / 36 = -0.017候选2:今天天气真的真的很好(长度10,sum_logprobs=-0.8)那么score2 = -0.8 / 10 ** 2 = -0.8 / 100 = -0.008此时score2 > score1,最终也会选择长度更长的序列2,但可以发现相比二、score2和score1的差值更大了,也就是说当self.length_penalty > 0的时候,其值越大,对长度更长的序列的得分增加的越多。
|
|
代码:
transformers/beam_search.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
def is_done(self, best_sum_logprobs: float, cur_len: int) -> bool:"""If there are enough hypotheses and that none of the hypotheses being generated can become better than the worstone in the heap, then we are done with this sentence."""if len(self) < self.num_beams:return Falseelif self.early_stopping:return Trueelse:cur_score = best_sum_logprobs / cur_len**self.length_penaltyret = self.worst_score >= cur_scorereturn ret
|
7-8行:若已生成序列个数小于 num_beams,返回 False;否则,若设置了提前停止,则返回 True;否则,判断已生成序列的最差得分是否大于等于当前步得分最高的序列的得分,若大于等于则返回 True,否则返回 False。其中 False 表示未解码完成,True 表示已解码完成; 返回当前步预测的 token,预测 token 对应的路径的得分和预测 token 所在路径的下标; 84-86行:从输出中获取当前步预测的 token,预测 token 对应的路径的得分和预测 token 所在路径的下标; 88-88行:更新 input_ids,即已生成的序列,将当前预测的 token 拼接到之前预测的序列之后,其中 input_ids[beam_idx, :] 表示通过所在路径的下标取出该路径已生成的 token 序列; 90-94行:更新 model_kwargs,用于下一次预测。若需要缓存已生成序列的 key-value 和 cross key-value,则根据 beam_idx 对其进行重排序,这是因为每一步预测的 token 所在的路径可能不一样,因此需要选出这些路径对应的 key value 进行缓存; 96-97行:将预测 token 当前所在的路径下标与该路径之前存储的路径下标进行拼接; 99-106行:与 greedy search 相同; 108-117行:从候选中选出最终需要返回的结果。 |
代码:
transformers/beam_search.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
def finalize(self,input_ids: torch.LongTensor,final_beam_scores: torch.FloatTensor,final_beam_tokens: torch.LongTensor,final_beam_indices: torch.LongTensor,max_length: int,pad_token_id: Optional[int] = None,eos_token_id: Optional[Union[int, List[int]]] = None,beam_indices: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,) -> Tuple[torch.LongTensor]:batch_size = len(self._beam_hyps)if isinstance(eos_token_id, int):eos_token_id = [eos_token_id]# finalize all open beam hypotheses and add to generated hypothesesfor batch_idx, beam_hyp in enumerate(self._beam_hyps):if self._done[batch_idx]:continue# all open beam hypotheses are added to the beam hypothesis# beam hypothesis class automatically keeps the best beamsfor beam_id in range(self.num_beams):batch_beam_idx = batch_idx * self.num_beams + beam_idfinal_score = final_beam_scores[batch_beam_idx].item()final_tokens = input_ids[batch_beam_idx]beam_index = beam_indices[batch_beam_idx] if beam_indices is not None else Nonebeam_hyp.add(final_tokens, final_score, beam_indices=beam_index)# select the best hypothesessent_lengths = input_ids.new(batch_size * self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep)best = []best_indices = []best_scores = torch.zeros(batch_size * self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep, device=self.device, dtype=torch.float32)# retrieve best hypothesesfor i, beam_hyp in enumerate(self._beam_hyps):sorted_hyps = sorted(beam_hyp.beams, key=lambda x: x[0])for j in range(self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep):best_hyp_tuple = sorted_hyps.pop()best_score = best_hyp_tuple[0]best_hyp = best_hyp_tuple[1]best_index = best_hyp_tuple[2]sent_lengths[self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep * i + j] = len(best_hyp)# append hyp to listsbest.append(best_hyp)# append indices to listbest_indices.append(best_index)best_scores[i * self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep + j] = best_score# prepare for adding eossent_lengths_max = sent_lengths.max().item() + 1sent_max_len = min(sent_lengths_max, max_length) if max_length is not None else sent_lengths_maxdecoded: torch.LongTensor = input_ids.new(batch_size * self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep, sent_max_len)if len(best_indices) > 0 and best_indices[0] is not None:indices: torch.LongTensor = input_ids.new(batch_size * self.num_beam_hyps_to_keep, sent_max_len)else:indices = None# shorter batches are padded if neededif sent_lengths.min().item() != sent_lengths.max().item():assert pad_token_id is not None, "`pad_token_id` has to be defined"decoded.fill_(pad_token_id)if indices is not None:indices.fill_(-1)# fill with hypotheses and eos_token_id if the latter fits infor i, (hypo, best_idx) in enumerate(zip(best, best_indices)):decoded[i, : sent_lengths[i]] = hypoif indices is not None:indices[i, : len(best_idx)] = torch.tensor(best_idx)if sent_lengths[i] < sent_max_len:# inserting only the first eos_token_iddecoded[i, sent_lengths[i]] = eos_token_id[0]return UserDict({"sequences": decoded,"sequence_scores": best_scores,"beam_indices": indices,})
|
|
3.3.3 解码结束,返回结果
if return_dict_in_generate:if not output_scores:sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"] = Noneif self.config.is_encoder_decoder:return BeamSearchEncoderDecoderOutput(sequences=sequence_outputs["sequences"],sequences_scores=sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"],scores=scores,beam_indices=sequence_outputs["beam_indices"],encoder_attentions=encoder_attentions,encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,decoder_attentions=decoder_attentions,cross_attentions=cross_attentions,decoder_hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return BeamSearchDecoderOnlyOutput(sequences=sequence_outputs["sequences"],sequences_scores=sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"],scores=scores,beam_indices=sequence_outputs["beam_indices"],attentions=decoder_attentions,hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return sequence_outputs["sequences"]
这一步的逻辑与 greedy search 基本一致;
3.4 整体流程
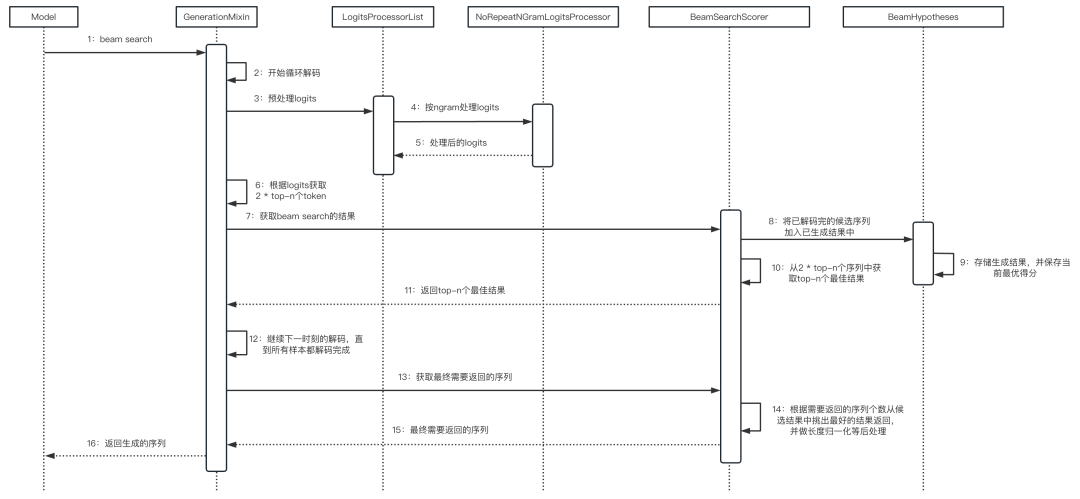
04
4.1 原理介绍
4.1.1 Random sampling
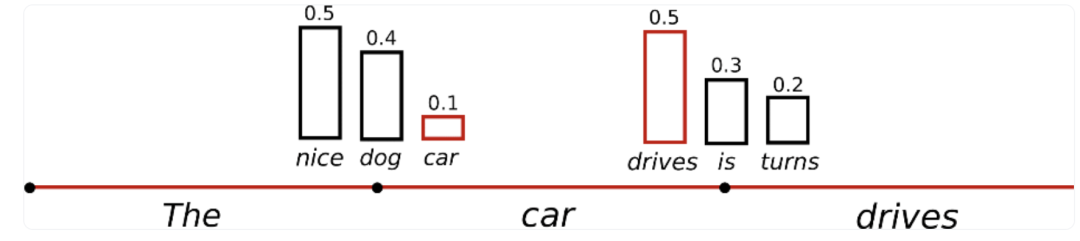
4.1.2 Top-k sampling

Fan et. al (2018) 提出了 Top-K 采样策略。该策略会在采样之前缩减采样空间,只保留概率最高的 k 个词,然后重新进行归一化得到新的概率分布。比如上图中,取 k=6,则只在6个词中进行采样,这6个词总概率有可能不高(左图),但也可能非常接近1(右图)。这会造成两个问题:
4.1.3 Top-p (Nucleus) sampling
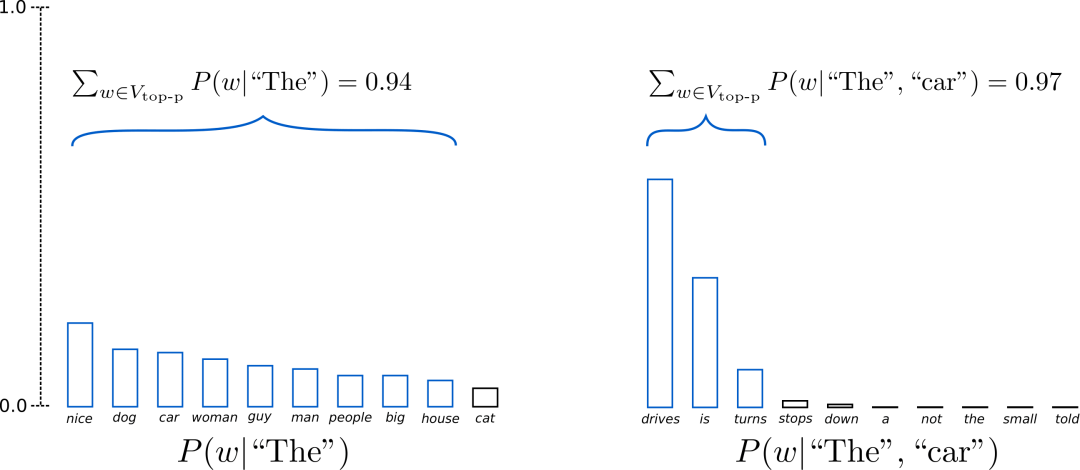
比如上图中,将阈值 p 设为0.9,左图会从9个候选词中筛选,右图会从3个候选词中筛选。
从本质上看,Top-p Sampling 和 Top-k Sampling 都是从缩小的候选 token 集合中 sample token,区别在于如何缩小候选集合。在实际使用中,top-k 和 top-p 有时也会同时使用,来避免采样到非常低概率的词,同时保证结果的多样性。
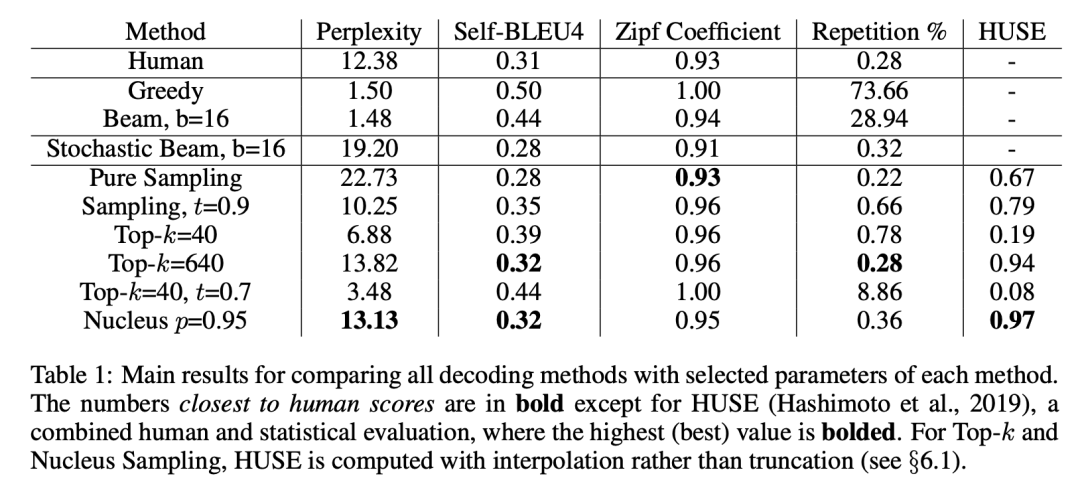
从上表中可以看出,top-p (nucleus)策略的结果是与 human 结果最相近的。并且有较低的重复率 repetition%。
4.2 快速上手
from transformers import (AutoTokenizer,AutoModelForCausalLM,LogitsProcessorList,MinLengthLogitsProcessor,TopKLogitsWarper,TopPLogitsWarper,TemperatureLogitsWarper,StoppingCriteriaList,MaxLengthCriteria,)import torchtokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2")# set pad_token_id to eos_token_id because GPT2 does not have a EOS tokenmodel.config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_idmodel.generation_config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_idinput_prompt = "Today is a beautiful day, and"input_ids = tokenizer(input_prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids# instantiate logits processorslogits_processor = LogitsProcessorList([MinLengthLogitsProcessor(15, eos_token_id=model.generation_config.eos_token_id),])# instantiate logits processorslogits_warper = LogitsProcessorList([TopKLogitsWarper(50),TopPLogitsWarper(0.9)])stopping_criteria = StoppingCriteriaList([MaxLengthCriteria(max_length=20)])torch.manual_seed(0)outputs = model.sample(input_ids,logits_processor=logits_processor,logits_warper=logits_warper,stopping_criteria=stopping_criteria,)result = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)print(result)-------------------------------------------------output-------------------------------------------------['Today is a beautiful day, and a wonderful day.nnI was lucky enough to meet the']
4.3 代码解读
4.3.1 基本设置,对后续需要使用的变量进行初始化
logits_warper = logits_warper if logits_warper is not None else LogitsProcessorList()这一步与 greedy search 基本相同,唯一区别在于初始化了一个 logits_warper;
4.3.2 从bos_token开始解码
# keep track of which sequences are already finishedunfinished_sequences = input_ids.new(input_ids.shape[0]).fill_(1)this_peer_finished = False # used by synced_gpus only# auto-regressive generationwhile True:if synced_gpus:# Under synced_gpus the `forward` call must continue until all gpus complete their sequence.# The following logic allows an early break if all peers finished generating their sequencethis_peer_finished_flag = torch.tensor(0.0 if this_peer_finished else 1.0).to(input_ids.device)# send 0.0 if we finished, 1.0 otherwisedist.all_reduce(this_peer_finished_flag, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)# did all peers finish? the reduced sum will be 0.0 thenif this_peer_finished_flag.item() == 0.0:break# prepare model inputsmodel_inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids, **model_kwargs)# forward pass to get next tokenoutputs = self(**model_inputs,return_dict=True,output_attentions=output_attentions,output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,)if synced_gpus and this_peer_finished:continue # don't waste resources running the code we don't neednext_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :]# pre-process distributionnext_token_scores = logits_processor(input_ids, next_token_logits)next_token_scores = logits_warper(input_ids, next_token_scores)# Store scores, attentions and hidden_states when requiredif return_dict_in_generate:if output_scores:scores += (next_token_scores,)if output_attentions:decoder_attentions += ((outputs.decoder_attentions,) if self.config.is_encoder_decoder else (outputs.attentions,))if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:cross_attentions += (outputs.cross_attentions,)if output_hidden_states:decoder_hidden_states += ((outputs.decoder_hidden_states,)if self.config.is_encoder_decoderelse (outputs.hidden_states,))# sampleprobs = nn.functional.softmax(next_token_scores, dim=-1)next_tokens = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1).squeeze(1)# finished sentences should have their next token be a padding tokenif eos_token_id is not None:if pad_token_id is None:raise ValueError("If `eos_token_id` is defined, make sure that `pad_token_id` is defined.")next_tokens = next_tokens * unfinished_sequences + pad_token_id * (1 - unfinished_sequences)# update generated ids, model inputs, and length for next stepinput_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_tokens[:, None]], dim=-1)model_kwargs = self._update_model_kwargs_for_generation(outputs, model_kwargs, is_encoder_decoder=self.config.is_encoder_decoder)# if eos_token was found in one sentence, set sentence to finishedif eos_token_id is not None:unfinished_sequences = unfinished_sequences.mul((sum(next_tokens != i for i in eos_token_id)).long())# stop when each sentence is finished, or if we exceed the maximum lengthif unfinished_sequences.max() == 0 or stopping_criteria(input_ids, scores):if not synced_gpus:breakelse:this_peer_finished = True
|
1-34行:与 greedy search 相同; 35-35行:根据采样方式对 next_token_scores 进行预处理,logits_wraper 同样为 LogitsProcessorList 的实例,会循环调用 LogitsProcessor 中的 processor,这里即为 wraper。 |
top-k
代码:
transformers/logits_process.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
class TopKLogitsWarper(LogitsWarper):r"""[`LogitsWarper`] that performs top-k, i.e. restricting to the k highest probability elements.Args:top_k (`int`):The number of highest probability vocabulary tokens to keep for top-k-filtering.filter_value (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `-float("Inf")`):All filtered values will be set to this float value.min_tokens_to_keep (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):Minimum number of tokens that cannot be filtered."""def __init__(self, top_k: int, filter_value: float = -float("Inf"), min_tokens_to_keep: int = 1):if not isinstance(top_k, int) or top_k <= 0:raise ValueError(f"`top_k` has to be a strictly positive integer, but is {top_k}")self.top_k = max(top_k, min_tokens_to_keep)self.filter_value = filter_valuedef __call__(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor, scores: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:top_k = min(self.top_k, scores.size(-1)) # Safety check# Remove all tokens with a probability less than the last token of the top-kindices_to_remove = scores < torch.topk(scores, top_k)[0][..., -1, None]scores = scores.masked_fill(indices_to_remove, self.filter_value)return scores
|
|
top-p
代码:
transformers/logits_process.py at v4.26.1 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
class TopPLogitsWarper(LogitsWarper):"""[`LogitsWarper`] that performs top-p, i.e. restricting to top tokens summing to prob_cut_off <= prob_cut_off.Args:top_p (`float`):If set to < 1, only the smallest set of most probable tokens with probabilities that add up to `top_p` orhigher are kept for generation.filter_value (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `-float("Inf")`):All filtered values will be set to this float value.min_tokens_to_keep (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):Minimum number of tokens that cannot be filtered."""def __init__(self, top_p: float, filter_value: float = -float("Inf"), min_tokens_to_keep: int = 1):top_p = float(top_p)if top_p < 0 or top_p > 1.0:raise ValueError(f"`top_p` has to be a float > 0 and < 1, but is {top_p}")self.top_p = top_pself.filter_value = filter_valueself.min_tokens_to_keep = min_tokens_to_keepdef __call__(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor, scores: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:sorted_logits, sorted_indices = torch.sort(scores, descending=False)cumulative_probs = sorted_logits.softmax(dim=-1).cumsum(dim=-1)# Remove tokens with cumulative top_p above the threshold (token with 0 are kept)sorted_indices_to_remove = cumulative_probs <= (1 - self.top_p)if self.min_tokens_to_keep > 1:# Keep at least min_tokens_to_keepsorted_indices_to_remove[..., -self.min_tokens_to_keep :] = 0# scatter sorted tensors to original indexingindices_to_remove = sorted_indices_to_remove.scatter(1, sorted_indices, sorted_indices_to_remove)scores = scores.masked_fill(indices_to_remove, self.filter_value)return scores
|
24-24行:对 scores 进行升序排序,获得 sorted_logits和sorted_indices,维度均为 [batch_size, vocab_size],即排序后的 logits 和对应在词表中的下标; 25-25行:对 sorted_logits 进行 softmax 归一化,获取每个 token 的预测概率值。之后计算 vocab_size 这一维度的累计和,举例来说,对于第一列,值不变,对于第二列,值为第一列和第二列的值相加,对于第三列,值为第一列、第二列和第三列的值相加,以此类推; 27-28行:获取需要移除的 token 的下标,即累计概率小于 1 – top_p 的列; 29-31行:若最少需要生成的 token 个数大于1,则将需要 sorted_indices_to_remove 的最后 self.min_tokens_to_keep 列重新赋值为0,表示这些列不移除; 33-34行:因为 sorted_indices_to_remove 是针对 sorted_indices 的,即此时需要移除的下标的并不是 vocab_size 中对应的下标,其值才对应真正需要移除的列,因此通过 scatter 来获取真正需要移除的 token 下标。 35-36行:将对应位置的 scores 赋值为 inf。最后返回预处理后的 scores; 37-53行:与 greedy search 相同; 55-57行:对 next_token_scores 计算概率值。根据概率值进行不放回采样,采样一个 token 作为预测 token; 59-80行:与 greedy search 相同。 |
4.3.3 解码结束,返回结果
if return_dict_in_generate:if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:return SampleEncoderDecoderOutput(sequences=input_ids,scores=scores,encoder_attentions=encoder_attentions,encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,decoder_attentions=decoder_attentions,cross_attentions=cross_attentions,decoder_hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return SampleDecoderOnlyOutput(sequences=input_ids,scores=scores,attentions=decoder_attentions,hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return input_ids
4.4 整体流程
05
5.1 原理介绍
Adiwardana et al., 2020 提出了 sample-and-rank 解码策略,该方法在对话领域效果很好。其思想是先通过 random sampling(结合temperature调整概率分布)生成出 N 个 sentence,然后再从 n 个 sentence 中选择概率乘积最大的。

beam sample 方法是 sample and rank 的改进,原理上类似,相比 sample and rank 在最后才对结果排序去获得最佳的 n 个序列,beam sample 在每一步保留当前最佳的 n 个序列,既保证了多样性和创造性,又可以减少在 rank 阶段需要过滤掉的句子。
5.2 快速上手
from transformers import (AutoTokenizer,AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,LogitsProcessorList,TopKLogitsWarper,TopPLogitsWarper,BeamSearchScorer,)import torchtokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-base")model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-base")encoder_input_str = "translate English to German: How old are you?"encoder_input_ids = tokenizer(encoder_input_str, return_tensors="pt").input_ids# lets run beam search using 3 beamsnum_beams = 3# define decoder start token idsinput_ids = torch.ones((num_beams, 1), device=model.device, dtype=torch.long)input_ids = input_ids * model.config.decoder_start_token_id# add encoder_outputs to model keyword argumentsmodel_kwargs = {"encoder_outputs": model.get_encoder()(encoder_input_ids.repeat_interleave(num_beams, dim=0), return_dict=True)}# instantiate beam scorerbeam_scorer = BeamSearchScorer(batch_size=1,max_length=model.config.max_length,num_beams=num_beams,device=model.device,)# instantiate logits processorslogits_warper = LogitsProcessorList([TopKLogitsWarper(50),TopPLogitsWarper(0.9),])outputs = model.beam_sample(input_ids, beam_scorer, logits_warper=logits_warper, **model_kwargs)result = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)print(result)-------------------------------------------------output-------------------------------------------------['Wie alt bist du?']
5.3 代码解读
代码地址:transformers/utils.py at ae54e3c3b18bac0832ad62ea9b896dfd52a09850 · huggingface/transformers · GitHub
5.3.1 基本设置,对后续需要使用的变量进行初始化
这一步与 beam search 相同。
5.3.2 从bos_token开始解码
beam_scores = torch.zeros((batch_size, num_beams), dtype=torch.float, device=input_ids.device)beam_scores = beam_scores.view((batch_size * num_beams,))this_peer_finished = False # used by synced_gpus onlywhile True:if synced_gpus:# Under synced_gpus the `forward` call must continue until all gpus complete their sequence.# The following logic allows an early break if all peers finished generating their sequencethis_peer_finished_flag = torch.tensor(0.0 if this_peer_finished else 1.0).to(input_ids.device)# send 0.0 if we finished, 1.0 otherwisedist.all_reduce(this_peer_finished_flag, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)# did all peers finish? the reduced sum will be 0.0 thenif this_peer_finished_flag.item() == 0.0:breakmodel_inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids, **model_kwargs)outputs = self(**model_inputs,return_dict=True,output_attentions=output_attentions,output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,)if synced_gpus and this_peer_finished:cur_len = cur_len + 1continue # don't waste resources running the code we don't neednext_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :]# hack: adjust tokens for Marian. For Marian we have to make sure that the `pad_token_id`# cannot be generated both before and after the `nn.functional.log_softmax` operation.next_token_logits = self.adjust_logits_during_generation(next_token_logits, cur_len=cur_len)next_token_scores = nn.functional.log_softmax(next_token_logits, dim=-1) # (batch_size * num_beams, vocab_size)next_token_scores_processed = logits_processor(input_ids, next_token_scores)next_token_scores = next_token_scores_processed + beam_scores[:, None].expand_as(next_token_scores)next_token_scores = logits_warper(input_ids, next_token_scores)# Store scores, attentions and hidden_states when requiredif return_dict_in_generate:if output_scores:scores += (logits_warper(input_ids, next_token_scores_processed),)if output_attentions:decoder_attentions += ((outputs.decoder_attentions,) if self.config.is_encoder_decoder else (outputs.attentions,))if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:cross_attentions += (outputs.cross_attentions,)if output_hidden_states:decoder_hidden_states += ((outputs.decoder_hidden_states,)if self.config.is_encoder_decoderelse (outputs.hidden_states,))# reshape for beam searchvocab_size = next_token_scores.shape[-1]next_token_scores = next_token_scores.view(batch_size, num_beams * vocab_size)probs = nn.functional.softmax(next_token_scores, dim=-1)next_tokens = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=2 * num_beams)next_token_scores = torch.gather(next_token_scores, -1, next_tokens)next_token_scores, _indices = torch.sort(next_token_scores, descending=True, dim=1)next_tokens = torch.gather(next_tokens, -1, _indices)next_indices = torch_int_div(next_tokens, vocab_size)next_tokens = next_tokens % vocab_size# statelessbeam_outputs = beam_scorer.process(input_ids,next_token_scores,next_tokens,next_indices,pad_token_id=pad_token_id,eos_token_id=eos_token_id,beam_indices=beam_indices,)beam_scores = beam_outputs["next_beam_scores"]beam_next_tokens = beam_outputs["next_beam_tokens"]beam_idx = beam_outputs["next_beam_indices"]input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids[beam_idx, :], beam_next_tokens.unsqueeze(-1)], dim=-1)model_kwargs = self._update_model_kwargs_for_generation(outputs, model_kwargs, is_encoder_decoder=self.config.is_encoder_decoder)if model_kwargs["past_key_values"] is not None:model_kwargs["past_key_values"] = self._reorder_cache(model_kwargs["past_key_values"], beam_idx)if return_dict_in_generate and output_scores:beam_indices = tuple((beam_indices[beam_idx[i]] + (beam_idx[i],) for i in range(len(beam_indices))))# increase cur_lencur_len = cur_len + 1if beam_scorer.is_done or stopping_criteria(input_ids, scores):if not synced_gpus:breakelse:this_peer_finished = Truesequence_outputs = beam_scorer.finalize(input_ids,beam_scores,next_tokens,next_indices,pad_token_id=pad_token_id,eos_token_id=eos_token_id,max_length=stopping_criteria.max_length,beam_indices=beam_indices,)
|
11-39行:与 beam search 基本一致; 40-40行:根据采样方式对 next_token_scores 进行预处理,logits_wrapper 为 LogitsProcessorList 的实例,已在 sample 中详细介绍; 42-62行:与 beam search 基本一致; 64-70行:这几行代码做的事情便是 sample and rank 中的 sample,首先对 next_token_scores 计算概率值,根据概率值进行不放回采样,采样 2 * num_beams个token 作为候选预测 token。之后根据 token id 去 gather 得到 token 对应的得分。因为采样得到的 token 不一定是按得分降序排序的,所以需要对 next_token_scores 降序排序,再根据 indices 去 gather 得到对应的 token,保证 token 是按得分降序排序的。 72-118行:与 beam search 基本一致。 |
5.3.3 解码结束,返回结果
if return_dict_in_generate:if not output_scores:sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"] = Noneif self.config.is_encoder_decoder:return BeamSampleEncoderDecoderOutput(sequences=sequence_outputs["sequences"],sequences_scores=sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"],scores=scores,beam_indices=sequence_outputs["beam_indices"],encoder_attentions=encoder_attentions,encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,decoder_attentions=decoder_attentions,cross_attentions=cross_attentions,decoder_hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return BeamSampleDecoderOnlyOutput(sequences=sequence_outputs["sequences"],sequences_scores=sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"],scores=scores,beam_indices=sequence_outputs["beam_indices"],attentions=decoder_attentions,hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return sequence_outputs["sequences"]
这一步的逻辑与 greedy search 基本一致;
5.4 整体流程
06
6.1 原理介绍

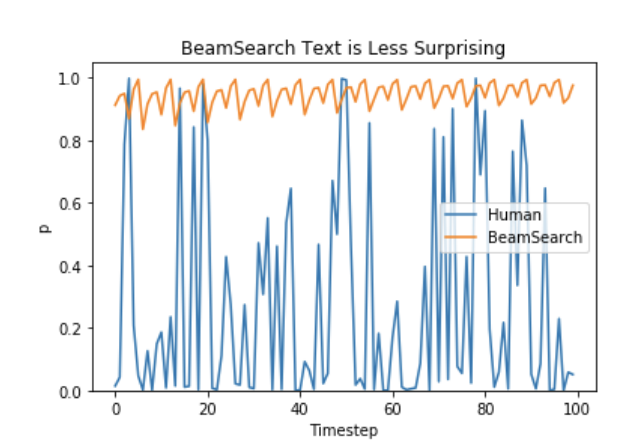
group beam search 主要思路是通过将 beam search 中的候选路径进行分组,在各组内去寻找最优解。如上图所示,beam search 的候选路径有6条,group beam search 将这6条候选路径两两作为一组,分为三组。每一步都在各组内的词表空间下去取 top-2 的结果作为当前预测的 token,对于当前组来说,通过对之前组已生成的 token 进行惩罚,来保证当前组生成的 token 与之前组不同的概率更大,从而更具多样性。
6.2 快速上手
from transformers import (AutoTokenizer,AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,LogitsProcessorList,MinLengthLogitsProcessor,HammingDiversityLogitsProcessor,BeamSearchScorer,)import torchtokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-base")model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-base")encoder_input_str = "translate English to German: How old are you?"encoder_input_ids = tokenizer(encoder_input_str, return_tensors="pt").input_ids# lets run diverse beam search using 6 beamsnum_beams = 6# define decoder start token idsinput_ids = torch.ones((num_beams, 1), device=model.device, dtype=torch.long)input_ids = input_ids * model.config.decoder_start_token_id# add encoder_outputs to model keyword argumentsmodel_kwargs = {"encoder_outputs": model.get_encoder()(encoder_input_ids.repeat_interleave(num_beams, dim=0), return_dict=True)}# instantiate beam scorerbeam_scorer = BeamSearchScorer(batch_size=1,max_length=model.config.max_length,num_beams=num_beams,device=model.device,num_beam_groups=3,num_beam_hyps_to_keep=2,)# instantiate logits processorslogits_processor = LogitsProcessorList([HammingDiversityLogitsProcessor(5.5, num_beams=6, num_beam_groups=3), ])outputs = model.group_beam_search(input_ids, beam_scorer, logits_processor=logits_processor, **model_kwargs)result = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)print(result)-------------------------------------------------output-------------------------------------------------['Wie alt bist du?', 'Wie alt sind Sie?']
6.3 代码解读
6.3.1 基本设置,对后续需要使用的变量进行初始化
batch_size = len(beam_scorer._beam_hyps)num_beams = beam_scorer.num_beamsnum_beam_groups = beam_scorer.num_beam_groupsnum_sub_beams = num_beams // num_beam_groups
|
|
6.3.2 从 bos_token 开始解码
# initialise score of first beam of each group with 0 and the rest with -1e9. This ensures that the beams in# the same group don't produce same tokens everytime.beam_scores = torch.full((batch_size, num_beams), -1e9, dtype=torch.float, device=device)beam_scores[:, ::num_sub_beams] = 0beam_scores = beam_scores.view((batch_size * num_beams,))this_peer_finished = False # used by synced_gpus onlywhile True:if synced_gpus:# Under synced_gpus the `forward` call must continue until all gpus complete their sequence.# The following logic allows an early break if all peers finished generating their sequencethis_peer_finished_flag = torch.tensor(0.0 if this_peer_finished else 1.0).to(input_ids.device)# send 0.0 if we finished, 1.0 otherwisedist.all_reduce(this_peer_finished_flag, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)# did all peers finish? the reduced sum will be 0.0 thenif this_peer_finished_flag.item() == 0.0:break# predicted tokens in cur_len stepcurrent_tokens = torch.zeros(batch_size * num_beams, dtype=input_ids.dtype, device=device)# indices which will form the beams in the next time stepreordering_indices = torch.zeros(batch_size * num_beams, dtype=torch.long, device=device)# do one decoder step on all beams of all sentences in batchmodel_inputs = self.prepare_inputs_for_generation(input_ids, **model_kwargs)outputs = self(**model_inputs,return_dict=True,output_attentions=output_attentions,output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,)if synced_gpus and this_peer_finished:cur_len = cur_len + 1continue # don't waste resources running the code we don't needif output_scores:processed_score = torch.zeros_like(outputs.logits[:, -1, :])for beam_group_idx in range(num_beam_groups):group_start_idx = beam_group_idx * num_sub_beamsgroup_end_idx = min(group_start_idx + num_sub_beams, num_beams)group_size = group_end_idx - group_start_idx# indices of beams of current group among all sentences in batchbatch_group_indices = []for batch_idx in range(batch_size):batch_group_indices.extend([batch_idx * num_beams + idx for idx in range(group_start_idx, group_end_idx)])group_input_ids = input_ids[batch_group_indices]# select outputs of beams of current group onlynext_token_logits = outputs.logits[batch_group_indices, -1, :]# hack: adjust tokens for Marian. For Marian we have to make sure that the `pad_token_id`# cannot be generated both before and after the `nn.functional.log_softmax` operation.next_token_logits = self.adjust_logits_during_generation(next_token_logits, cur_len=cur_len)next_token_scores = nn.functional.log_softmax(next_token_logits, dim=-1) # (batch_size * group_size, vocab_size)vocab_size = next_token_scores.shape[-1]next_token_scores_processed = logits_processor(group_input_ids, next_token_scores, current_tokens=current_tokens, beam_group_idx=beam_group_idx)next_token_scores = next_token_scores_processed + beam_scores[batch_group_indices].unsqueeze(-1)next_token_scores = next_token_scores.expand_as(next_token_scores_processed)if output_scores:processed_score[batch_group_indices] = next_token_scores_processed# reshape for beam searchnext_token_scores = next_token_scores.view(batch_size, group_size * vocab_size)# Sample 2 next tokens for each beam (so we have some spare tokens and match output of beam search)next_token_scores, next_tokens = torch.topk(next_token_scores, 2 * group_size, dim=1, largest=True, sorted=True)next_indices = torch_int_div(next_tokens, vocab_size)next_tokens = next_tokens % vocab_size# statelessprocess_beam_indices = sum(beam_indices, ()) if beam_indices is not None else Nonebeam_outputs = beam_scorer.process(group_input_ids,next_token_scores,next_tokens,next_indices,pad_token_id=pad_token_id,eos_token_id=eos_token_id,beam_indices=process_beam_indices,)beam_scores[batch_group_indices] = beam_outputs["next_beam_scores"]beam_next_tokens = beam_outputs["next_beam_tokens"]beam_idx = beam_outputs["next_beam_indices"]if return_dict_in_generate and output_scores:beam_indices[beam_group_idx] = tuple(beam_indices[beam_group_idx][beam_idx[i]] + (beam_idx[i],) for i in range(len(beam_indices[0])))input_ids[batch_group_indices] = group_input_ids[beam_idx]group_input_ids = torch.cat([group_input_ids[beam_idx, :], beam_next_tokens.unsqueeze(-1)], dim=-1)current_tokens[batch_group_indices] = group_input_ids[:, -1]# (beam_idx // group_size) -> batch_idx# (beam_idx % group_size) -> offset of idx inside the groupreordering_indices[batch_group_indices] = (num_beams * torch_int_div(beam_idx, group_size) + group_start_idx + (beam_idx % group_size))# Store scores, attentions and hidden_states when requiredif return_dict_in_generate:if output_scores:scores += (processed_score,)if output_attentions:decoder_attentions += ((outputs.decoder_attentions,) if self.config.is_encoder_decoder else (outputs.attentions,))if self.config.is_encoder_decoder:cross_attentions += (outputs.cross_attentions,)if output_hidden_states:decoder_hidden_states += ((outputs.decoder_hidden_states,)if self.config.is_encoder_decoderelse (outputs.hidden_states,))input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, current_tokens.unsqueeze(-1)], dim=-1)model_kwargs = self._update_model_kwargs_for_generation(outputs, model_kwargs, is_encoder_decoder=self.config.is_encoder_decoder)if model_kwargs["past_key_values"] is not None:model_kwargs["past_key_values"] = self._reorder_cache(model_kwargs["past_key_values"], reordering_indices)# increase cur_lencur_len = cur_len + 1if beam_scorer.is_done or stopping_criteria(input_ids, scores):if not synced_gpus:breakelse:this_peer_finished = Truefinal_beam_indices = sum(beam_indices, ()) if beam_indices is not None else Nonesequence_outputs = beam_scorer.finalize(input_ids,beam_scores,next_tokens,next_indices,pad_token_id=pad_token_id,eos_token_id=eos_token_id,max_length=stopping_criteria.max_length,beam_indices=final_beam_indices,)
|
1-5行:初始化 beam_scores,维度为 [batch_size, num_beams] ,首先赋值为-1e9,之后将第一条候选路径的路径分数均赋值为0,含义已在 beam search 中介绍; 7-17行:与 beam search 基本一致; 19-20行:初始化 current_tokens,用于存储当前步预测的 token; 22-23行:初始化 reordering_indices,用于后续对缓存的 key value 进行重排序; 25-39行:与 beam search 基本一致; 41-41行:在组级别进行遍历; 42-44行:初始化组的位置和大小信息,beam_group_idx 表示当前是第几组,num_sub_beams 表示每组的候选路径个数,因此 group_start_idx 表示对于一个样本来说,该组在其候选路径中的起始位置,group_end_idx 为该组在其候选路径中的结束位置,左闭右开,group_size 是组的大小,即组内有多少候选路径,注意这里组的大小是针对单个样本的; 46-53行:因为每个样本的所有候选路径会被分成多个组,所以这里是在将所有样本属于该组的候选路径在 batch 内的下标加入到 batch_group_indices 中。通过下标将每个样本属于该组的候选路径从 input_ids 中取出来,加入到 group_input_ids,大小为group_size * batch_size; 55-56行:取出该组内所有样本在当前步的 logits; 58-104行:与 beam search 基本一致,最后得到的 beam_scores 是预测token的得分,beam_next_tokens 是预测 token 的 id,beam_idx 是预测 token 在 group_input_ids 中的下标。需要额外介绍的是66-67行对 logits 的预处理,快速上手中使用的预处理方法为 Hamming 多样性预处理方法,这个方法也只针对 group beam search使用,作用是使得各个组生成的结果更加具有多样性;与 beam search 基本一致,最后得到的 beam_scores 是预测 token 的得分,beam_next_tokens 是预测 token 的 id,beam_idx 是预测 token 在 group_input_ids 中的下标。需要额外介绍的是66-67行对 logits 的预处理,快速上手中使用的预处理方法为 Hamming 多样性预处理方法,这个方法也只针对 group beam search 使用,作用是使得各个组生成的结果更加具有多样性。 |
class HammingDiversityLogitsProcessor(LogitsProcessor):r"""[`LogitsProcessor`] that enforces diverse beam search. Note that this logits processor is only effective for[`PreTrainedModel.group_beam_search`]. See [Diverse Beam Search: Decoding Diverse Solutions from Neural SequenceModels](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02424.pdf) for more details.Args:diversity_penalty (`float`):This value is subtracted from a beam's score if it generates a token same as any beam from other group at aparticular time. Note that `diversity_penalty` is only effective if `group beam search` is enabled.num_beams (`int`):Number of beams used for group beam search. See [this paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02424.pdf) for moredetails.num_beam_groups (`int`):Number of groups to divide `num_beams` into in order to ensure diversity among different groups of beams.See [this paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02424.pdf) for more details."""def __init__(self, diversity_penalty: float, num_beams: int, num_beam_groups: int):if not isinstance(diversity_penalty, float) or (not diversity_penalty > 0.0):raise ValueError("`diversity_penalty` should be a float strictly larger than 0.")self._diversity_penalty = diversity_penaltyif not isinstance(num_beams, int) or num_beams < 2:raise ValueError("`num_beams` should be an integer strictly larger than 1.")self._num_beams = num_beamsif not isinstance(num_beam_groups, int) or num_beam_groups < 2:raise ValueError("`num_beam_groups` should be an integer strictly larger than 1.")if num_beam_groups > num_beams:raise ValueError("`beam_groups` has to be smaller or equal to `num_beams`.")self._num_sub_beams = num_beams // num_beam_groupsdef __call__(self,input_ids: torch.LongTensor,scores: torch.FloatTensor,current_tokens: torch.LongTensor,beam_group_idx: int,) -> torch.FloatTensor:# hamming diversity: penalise using same token in current group which was used in previous groups at# the same time stepbatch_size = current_tokens.shape[0] // self._num_beamsgroup_start_idx = beam_group_idx * self._num_sub_beamsgroup_end_idx = min(group_start_idx + self._num_sub_beams, self._num_beams)group_size = group_end_idx - group_start_idxvocab_size = scores.shape[-1]if group_start_idx == 0:return scoresfor batch_idx in range(batch_size):# predicted tokens of last time step of previous groupsprevious_group_tokens = current_tokens[batch_idx * self._num_beams : batch_idx * self._num_beams + group_start_idx]token_frequency = torch.bincount(previous_group_tokens, minlength=vocab_size).to(scores.device)scores[batch_idx * group_size : (batch_idx + 1) * group_size] -= self._diversity_penalty * token_frequencyreturn scores
|
|
6.3.3 解码结束,返回结果
if return_dict_in_generate:if not output_scores:sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"] = Noneif self.config.is_encoder_decoder:return BeamSearchEncoderDecoderOutput(sequences=sequence_outputs["sequences"],sequences_scores=sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"],scores=scores,beam_indices=sequence_outputs["beam_indices"],encoder_attentions=encoder_attentions,encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,decoder_attentions=decoder_attentions,cross_attentions=cross_attentions,decoder_hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return BeamSearchDecoderOnlyOutput(sequences=sequence_outputs["sequences"],sequences_scores=sequence_outputs["sequence_scores"],scores=scores,beam_indices=sequence_outputs["beam_indices"],attentions=decoder_attentions,hidden_states=decoder_hidden_states,)else:return sequence_outputs["sequences"]
这一步的逻辑与 greedy search 基本一致;
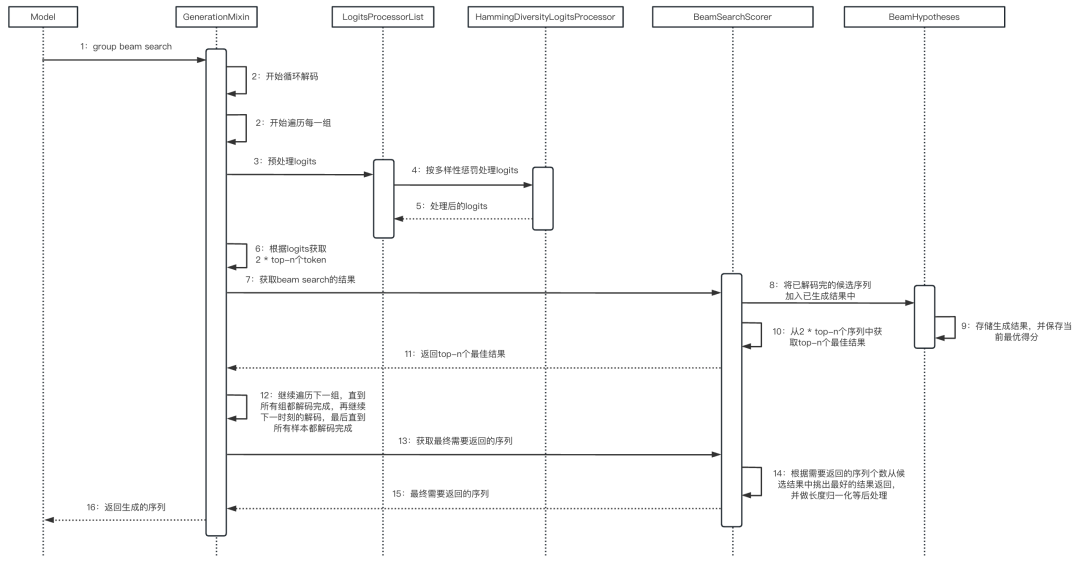
6.4 整体流程
整体流程如下面的时序图所示: 07
总结 通过前面的介绍,相信大家已经发现了,各种解码策略无非是通过调整 logits(即模型对每个 token 的预测得分)和 batch_size,来获得不同的生成结果。
对 logits 做调整一般又可分为是用于预处理还是采样,对用于预处理的最小长度、重复词惩罚这些功能,抽象出基类 Processor 类,对用于采样的 top-k、top-p 这些功能,抽象出基类 Warper。而所有对 logits 做调整的功能类都可以又加入到 LogitsProcessList,组成一个 pipeline,每次想用哪一个对其进行初始化并加入即可。
对 batch_size 做调整主要在需要生成多个候选或是需要返回多个结果的情况下,对于 beam search 系列的解码策略,通过将 batch_size 扩大候选路径的个数倍,来获得不同的候选序列。对 sample 系列的解码策略,通过将 batch_size 扩大返回结果个数倍,来采样得到不同的结果。
08
主流模型方案 以上方案被主流模型所采用。下面表格罗列了从公开论文中梳理出的解码方案:
| 模型 | 解码策略 | 备注 |
| GPT-2(OpenAI) | greedy decoding | 阅读理解任务和翻译任务 |
| GPT-3(OpenAI) | top-p sampling | temperature=1, p=0.9 |
| Meena (Google) | sample-and-rank | N=20,temperature=0.88,random sampling |
| LaMDA (Google) | sample-and-rank | N=16,temperature=1,top-k sampling, k=40 |
| LLaMA (Meta) | greedy decoding | Question Answering 任务,其它任务不明 |
参考文献
– END –
报告下载

大佬观点